Newly-Launched U. S. Nanosatellites Could Play Pivotal Role in Tracking Hypersonic, Ballistic Missiles

The Pentagon says the two nanosatellites or “CubeSats” that was launched by the Missile Defense Agency (MDA) on June 30 into low-earth orbit (LEO) could play a large role in tracking and destroying the enemy’s hypersonic and ballistic missiles.
The announcement comes as Russia inches closer to induct its powerful S-500 system, that it claims can destroy ICBMs, hypersonic missiles and LEO satellites.
The CubeSat Networked Communications Experiment (CNCE) Block 1 — part of MDA's Nanosat Testbed Initiative (NTI) — uses small, low-cost satellites to demonstrate networked radio communications between nanosatellites while in orbit. MDA will conduct a 90-day demonstration, with a mission extension of up to one year, to ensure the two CubeSats can navigate properly, receive and send signals to radios and networks and operate as intended.
"These satellites will test key technologies that mitigate risk for systems, such as the Hypersonic and Ballistic Tracking Space Sensor," Walt Chai, MDA director for space sensors, said. "The CNCE Block 1 mission will demonstrate the viability of advanced communications technologies using reduced size, weight and power in support of missile defense communications architectures."
MDA is developing the Hypersonic and Ballistic Tracking Space Sensor payload. When eventually deployed on satellites in low earth orbit, it will detect and track hypersonic and ballistic missile threats and provide critical data to the Missile Defense System and the warfighter.
"The missile defense architecture will require communications between interceptors, sensors and command and control systems to quickly identify, track and destroy incoming enemy missiles before they reach their targets. The CubeSats will allow the agency to demonstrate the capabilities quickly and affordably," Chai said.
CubeSat missions allow for flexibility that includes rapid follow-on flights featuring planned, incremental technology improvements with overall greater cost efficiency than using larger, more traditional satellites.
"For the NTI efforts, we only need something small to take technology experiments to space in order to test in the relevant environment and gather accurate data. CubeSats are the perfect platform for this,” Shari Feth, head of the Innovation, Science and Technology directorate at MDA, said.
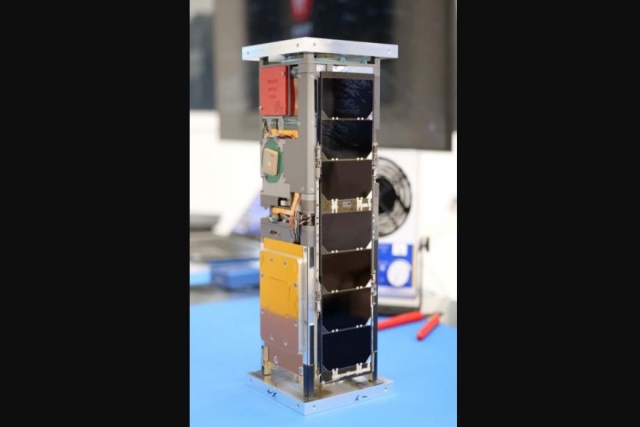

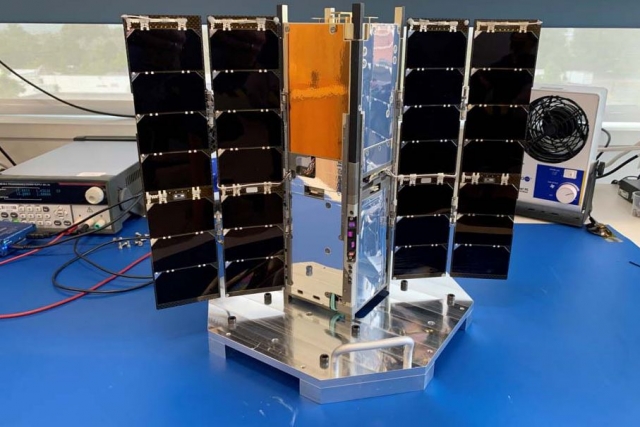
CubeSats are a subset of the small satellite family of satellite systems known as nanosatellites. A small satellite is generally considered to be any satellite that weighs less than 300kg. Within the small satellite family, CubeSats are defined by standardized characteristics such as shape, size and weight.
The standard CubeSat "unit" is referred to as a 1U. A 1U CubeSat is a 10 centimeter cube with a mass of up to about 1.33-1.5 kg. CubeSats typically range in size from 1U to no more than 27U in size.
By conforming to very specific CubeSat standards, reduced mission costs are realized — including costs associated with transporting CubeSats to, and deploying them into space, Feth said.
Most CubeSats are produced as commercial off-the-shelf products. This is due, in part, to the standardization inherent to CubeSats, making mass-produced components and off-the-shelf parts attractive for commercial vendor production.
The cost per satellite is about $1.3 million versus hundreds of millions required for traditional satellite construction. The hardware was built, and the bus and payloads were integrated, under a Rapid Innovation Fund contract.
"The ability to leverage the rapid advances in commercial CubeSat technology, as well as the growing base of commercial small launch providers, enables a unique testing capability never before available," Eric Cole, NTI project lead for MDA, said. "The ability to test in the relevant environment of space enables testing to achieve higher technology readiness levels, making the technology transition path into operational systems much more viable."
According to Jeff Keller, chief engineer for technology maturation at MDA, a primary advantage to maturing technology through NTI is the ability to divide complex challenges into discrete parts. "This allows us to effectively balance risk and cost by utilizing a series of phased demonstrations. Each mission leverages lessons learned from the previous mission," he said.
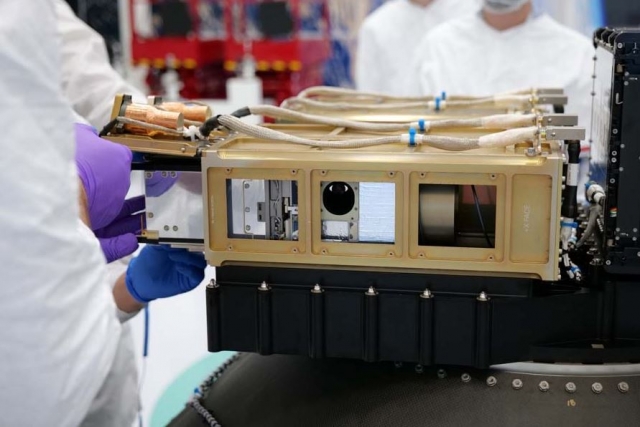

The overall result is that engineering and development of CubeSats is less costly than more highly customized small satellites. CubeSat payloads also enjoy the cost benefits from commercial CubeSat technology, but they tend to be more specialized for the missions selected by the CubeSat user.
Commercial applications for CubeSats range from communications, remote sensing to environmental applications. For MDA's CNCE Block 1 experiment, there could be commercial applications for the communications technologies being demonstrated, Feth said.
"We leveraged the department's Small Business Innovation Research and Rapid Innovation Funding programs to select the cutting edge CubeSat vendors," Yazmin Carroll, director of MDA's technology maturation unit, said. “The vendors provide the spacecraft and payloads to meet the NTI mission needs in support of key missile defense technology maturation."
MDA and industry have worked together to uniquely define and tailor a quality, safety, and mission-assurance approach to balance risk and technology development costs. MDA and industry have also worked together to align industry standards and best practices to improve CubeSat technology development efforts, Keller said.
The CubeSats went to space aboard a VOX Space LLC, a subsidiary of Virgin Orbit, LauncherOne rocket as part of a payload-sharing arrangement with the DOD Space Test Program.
Other agencies involved in CNCE Block 1's CubeSat development and experimentation are: defense department-led Mobile CubeSat Command and Control, or MC3, ground station network, Space Dynamics laboratory (Mission Integrator), Space Micro Inc. (Payload) and Blue Canyon Technologies (Spacecraft Bus).